Management guidelines for pulmonary irAEs
Common pulmonary irAE symptoms
International guideline (ASCO, ESMO and NCCN) recommendations for pulmonary irAEs1-3 ^
^ For detailed guidelines, please refer to original publication
| NCCN1 | ESMO2 | ASCO3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Consider holding immunotherapy | Consider delaying immunotherapy If symptoms worsen, treat as grade 2 |
Consider holding immunotherapy If no improvement, treat as Grade 2 |
| Grade 2 | Hold immunotherapy | ||
| Consider empiric antibiotics if infection is suspected | |||
| Prednisone/IV methylprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg/day* | Oral prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day* | Prednisone 1–2 mg/kg/day and taper over 4–6 weeks* | |
| If no improvement after 48–72 hours of recommended corticosteroids, treat as Grade 3 Consider pulmonary consultation |
If no improvement after 48 hours of recommended corticosteroids, treat as Grade 3 Consider pneumocystis prophylaxis |
If no improvement after 48–72 hours of recommended corticosteroids, treat as Grade 3 Consider pulmonary and infectious disease consultation |
|
| Grade 3/4 | Discontinue immunotherapy Consider empiric antibiotics Methylprednisolone IV 1–2 mg/kg/day* If no improvement, consider infliximab, IVIG, MMF, cyclophosphamide Hospitalise |
||
| Consult pulmonary and infectious disease | - | Consult pulmonary and infectious disease | |
*Consult ‘Steroid and immunosuppressor usage’ table for more information
ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; IV, intravenous; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
Diagnostic assessment may include chest x-ray, CT, pulse oximetry, blood panels (FBC/UEC/LFTs/TFTs/Ca/ESR/CRP),2 nasal swabs, sputum and urine testing.1-3 ESMO recommends considering a sputum sample and screening for infectious causes even at the Grade 1 level2; ASCO and the NCCN recommend these investigations only at Grade ≥2.1,3
|
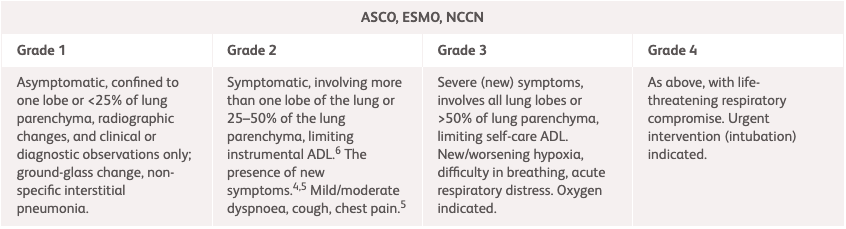
NCCN, ESMO, ASCO1-3 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 |
| Asymptomatic, confined to one lobe or <25% of lung parenchyma.1-3 Clinical or diagnostic observations only.3 |
Symptomatic, involving more than one lobe of the lung or 25–50% of the lung parenchyma; medical intervention indicated; limiting instrumental ADL.3 The presence of new or worsening symptoms.1,2 Dyspnoea, shortness of breath, cough, chest pain, increased oxygen requirement.2 Consider cardiac etiologies.1 |
Severe (new) symptoms.1-3 Involves all lung lobes or >50% of lung parenchyma, limiting self-care ADL, new/worsening hypoxia, oxygen indicated.1,3 Difficulty in breathing, acute respiratory distress.2 |
As Grade 3, with life-threatening respiratory compromise1-3. Urgent intervention (intubation) indicated.3 |
ADL, activities of daily living; ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; Ca, calcium; CRP, C-reactive protein; CT, computed tomography; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; FBC, full blood count; LFT, liver function test; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; TFT, thyroid function test; UEC, urea, electrolytes, creatinine.
| NCCN1 | ESMO2 | ASCO3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Reassess history, conduct a physical examination and pulse oximetry on the schedule indicated below, plus any supplementary investigations as described. | ||
| Within 1–2 weeks. Consider a chest CT with contrast, and repeat CT in 4–6 weeks or if clinically indicated by patient developing symptoms. |
Every 2–3 days. Baseline indications:
Consider sputum and screening for viral, opportunistic or specific bacterials infections (Mycoplasma, Legionella) depending on the clinical context. |
Weekly. May offer chest x-ray. May offer repeat CT in 3–4 weeks as well as repeat spirometry/DLCO if done at baseline. |
|
| Grade 2 | Every 3–7 days with H&P and pulse oximetry. Consider chest CT with contrast and repeat chest CT in 3–4 weeks. |
Daily. Outpatient monitoring: Chest CT with contrast, consider infection work (sputum, blood and urine culture);consider bronchoscopy with BAL to rule out infection and tumour infiltration. Baseline indications: as grade 1, with the addition of repeating chest x-ray weekly, baseline blood tests and LFTs including TLCO. |
At least once per week. Consider bronchoscopy with BAL ± transbronchial biopsy |
| Grade 3–4 | At these grades, patients should be admitted for inpatient care/hospitalised and receiving active medical intervention. If feasible, continue to conduct tests as recommended above. | ||
ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; CT, computed tomography; DLCO, diffusing capacity of lung for carbon monoxide; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; LFT, liver function test; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; TCLO, transfer factor for carbon monoxide.
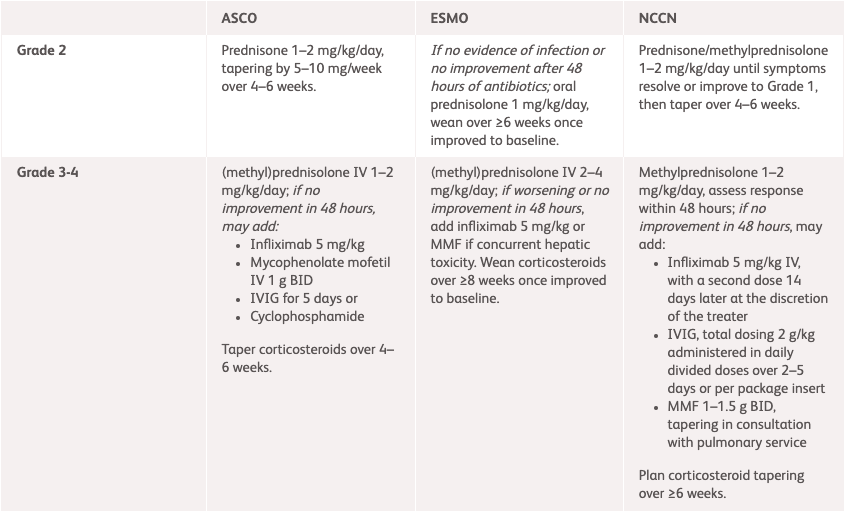
| NCCN1 | ESMO2 | ASCO3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 2 | Prednisone/methylprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg/day until symptoms improve to Grade 1, then taper over 4–6 weeks. |
If no evidence of infection or no improvement after 48 hours of antibiotics:
oral prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day, wean over 4–6 weeks once improved to baseline. |
Prednisone 1–2 mg/kg/day, tapering over 4–6 weeks.* |
| Grade 3–4 |
Methylprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg/day, assess response within 48 hours If no improvement in 48 hours, may add:
Plan corticosteroid tapering over ≥6 weeks. |
(methyl)prednisolone IV 1–2 mg/kg/day If no improvement in 48 hours, may add:
Consider MMF or cyclophosphamide. |
(methyl)prednisolone IV 1–2 mg/kg/day If no improvement in 48 hours, may add:
Taper corticosteroids over 4–6 weeks.* |
*Subset of patients may develop chronic pneumonitis and may require longer taper. Chronic pneumonitis is a described phenomenon where the incidence is not known but <2%.3
†Supplement calcium and vitamin D as per local guidelines; For pneumocystis prophylaxis use cotrimoxazole 480 mg BID on Monday, Wednesday and Friday or inhaled pentamidine if cotrimoxazole allergy is present.2
ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; BID, twice daily; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; IV, intravenous; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; PO, orally.
References:
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Management of immunotherapy-Related Toxicities. Version 1.2025. Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/immunotherapy.pdf. Accessed March 2025.
- Haanen J, et al. Ann Oncol 2022;33:1217–1238. Available at: https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(22)04187-4/fulltext. Accessed March 2025.
- Schneider BJ, et al. J Clin Oncol 2021;39:4073–4126. Available at: https://ascopubs.org/doi/full/10.1200/JCO.21.01440. Accessed March 2025.
- OPDIVO® (nivolumab) Product Information, BMS Hong Kong.
- YERVOY® (ipilumab) Product Information, BMS Hong Kong.