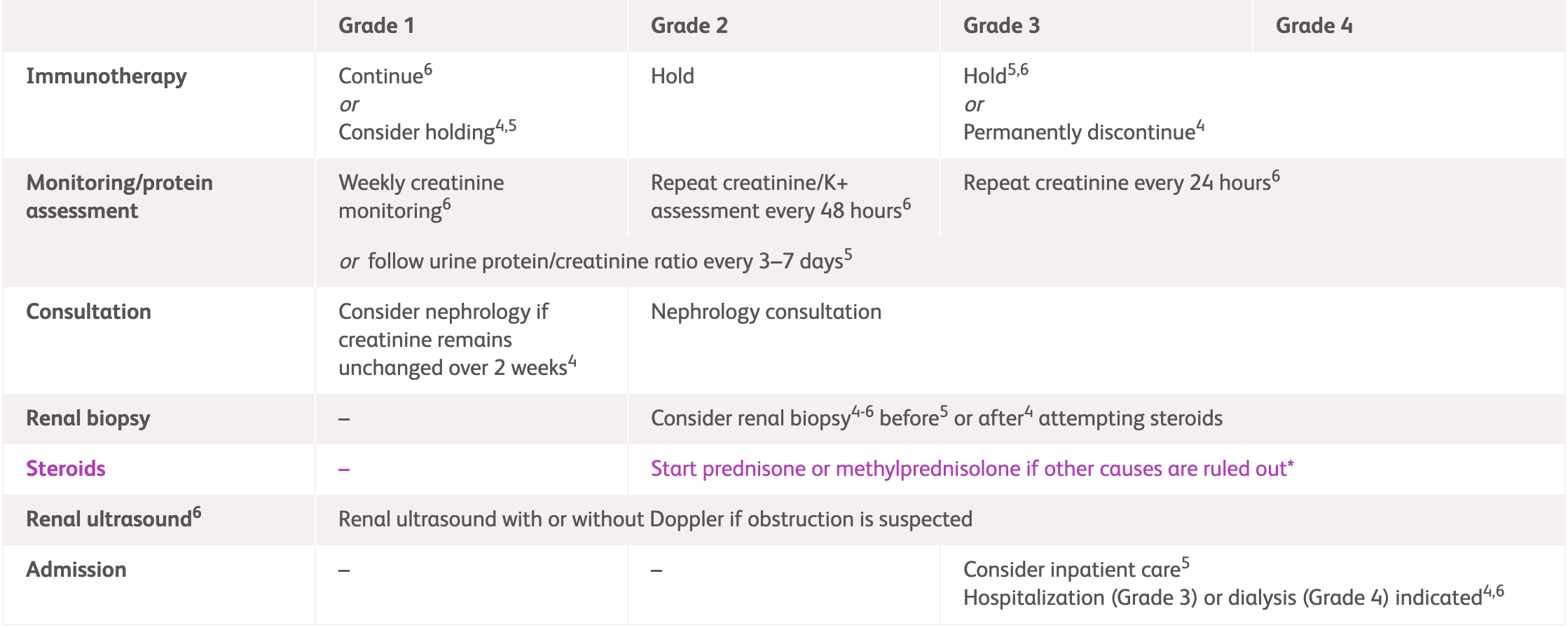
Management guidelines for renal irAEs
Common renal irAE symptoms
International guideline (ASCO, ESMO and NCCN) recommendations for renal irAEs1–3 ^
^ For detailed guidelines, please refer to original publication
| NCCN2* | ESMO3 | ASCO1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | Limit/discontinue nephrotoxic medications1-3 and dose adjust to avoid creatinine clearance2 | |||
| Check serum creatinine every 3–7 days Avoid PPIs (use H2 blockers for GI prophylaxis) Consider increased oral/IV hydration and reassess |
Monitor creatinine weekly Reflex kidney biopsy should be discouraged until steroid treatment has been attempted |
|||
| Grade 1 | Consider holding immunotherapy | Continue immunotherapy Review creatinine weekly |
Consider holding immunotherapy | |
| Consider nephrology consultation if sustained elevation of creatinine | Review hydration status, medications, urine test and culture if UTI symptoms Dipstick urine and send for protein assessment Conduct UPCR If obstruction suspected: renal ultrasound ± doppler to exclude obstruction or clot |
|||
| Grade 2 | Hold immunotherapy Nephrology consultation Corticosteroid use† |
|||
| Consider renal biopsy | Consider renal biopsy Increase hydration Review creatinine and K+ every 48 hours Tests as described in Grade 1 If proteinuria: 24-hour collection/ UPCR If blood: phase contrast microscopy and GN screen if nephrologist recommends |
Evaluate for other causes (recent IV contrast, medications, and fluid status) | ||
| Grade 3/4 ‡ | Hold/discontinue immunotherapy Corticosteroid use† Nephrology consultation |
|||
| Consider inpatient care Consider renal biopsy if no improvement within 5–7 days and/or new proteinuria Based on biopsy results, consider adding one of the following if kidney injury remains >Grade 2 after 4–6 weeks of steroids or creatinine increases during steroid taper (or once off steroids):
|
Admit patient Consider renal biopsy. Assess creatinine every 24 hours At grade 4, patients should be admitted to a hospital where renal replacement therapy is available |
Evaluate for other causes (recent IV contrast, medications, fluid status, and UTI) | ||
*Note that for NCCN guidelines, grading for immuno-oncology-related renal adverse events range from Stage 1 to 3.
†Consult steroid usage table below for more information.
‡In all cases, increase the urgency of testing and intervention in Grade 4 patients.
ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; GI, gastrointestinal; GN, glomerulonephritis; H2, histamine-2 receptor antagonists; IV, intravenous; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; PPIs, proton pump inhibitors; UPCR, urine protein-to-creatinine ratio; UTI, urinary tract infection; SCR, serum creatinine; ULN, upper limit of normal.
| NCCN2* | ESMO3 | ASCO1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | 1.5–2× baseline creatinine or increase of ≥0.3 mg/dL over 48 hours. | CTCAE: Creatinine >1–1.5× ULN KDIGO: Increase in SCr >0.3 mg/dL within 48 hours or 1.5–1.9× baseline |
Creatinine level increase of >0.3 mg/dL or 1.5–2.0× above baseline |
| Grade 2 | 2–3× baseline creatinine | CTCAE: Creatinine >1.5–3.0× baseline or >1.5–3.0× ULN KDIGO: Increase in SCr to 2.0–2.9× baseline |
Creatinine 2–3× above baseline |
| Grade 3 | ≥3.0× baseline creatinine; 4.0 mg/dL or need for RRT | CTCAE: Creatinine >3× baseline or >3–6× ULN KDIGO: Increase in SCr to 3× baseline or to >4.0 mg/dL or initiation of dialysis |
Creatinine >3× baseline or >4.0 mg/dL or hospitalisation indicated |
| Grade 4 | ~ | CTCAE: Creatinine >6× ULN | Life-threatening consequences: dialysis indicated; creatinine 6× above baseline |
*Note that for NCCN guidelines, grading for immunooncology-related renal adverse events range from Stage 1 to 3.
ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; CTCAE, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; KDIGO, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; RRT, renal replacement therapy; SCR, serum creatinine; ULN, upper limit of normal.
| NCCN2* | ESMO3 | ASCO1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 2 | Prednisone 0.5–1 mg/kg/day If persistent beyond 1 week, use prednisone/IV methylprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg/day |
Oral prednisolone 0.5–1 mg/kg if renal biopsy indicates immune-related adverse event | 0.5–1 mg/kg/day prednisone equivalents (if other aetiologies are ruled out) If no improvement by 1 week, increase to 1–2 mg/kg/day prednisone equivalents and permanently discontinue immunotherapy If improved to grade 1, taper steroids over at least 4 weeks If elevations persist greater than 1 week or worsen, treat as grade 3 |
| Grade 3 | Prednisone/IV methylprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg/day If injury remains >grade 2 after 4–6 weeks of steroids or creatinine increases during steroid taper (or once off steroids)
|
Initiate IV methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg or pulse dose CSs of 250–500 mg methylprednisolone for 3 days | 1–2 mg/kg/day prednisone or equivalent If elevations persist >3–5 days or worsen, consider additional immunosuppression such as infliximab, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate If improved to grade 1, taper steroids over at least 4 weeks |
| Grade 4 | ~ | As per grade 3 | If elevations persist >3–5 days or worsen, consider additional immunosuppression such as infliximab, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate If improved to grade 1, taper steroids over at least 4 weeks |
*Note that for NCCN guidelines, grading for immunooncology-related renal adverse events range from Stage 1 to 3.
ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; CS, corticosteroid; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; IV, intravenous; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
References:
- Schneider BJ, et al. J Clin Oncol 2021;39:4073–4126. Available at: https://ascopubs.org/doi/full/10.1200/JCO.21.01440. Accessed April 2025.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Management of immunotherapy-Related Toxicities. Version 1.2025. Available: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/immunotherapy.pdf. Accessed 13 April 2025.
- Haanen J, et al. Ann Oncol 2022;33:1217–1238. Available at: https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(22)04187-4/fulltext. Accessed March 2025.
- OPDIVO® (nivolumab) Product Information, BMS Hong Kong.
- YERVOY® (ipilumab) Product Information, BMS Hong Kong.