Management guidelines for hepatic irAEs
Common hepatic irAE symptom
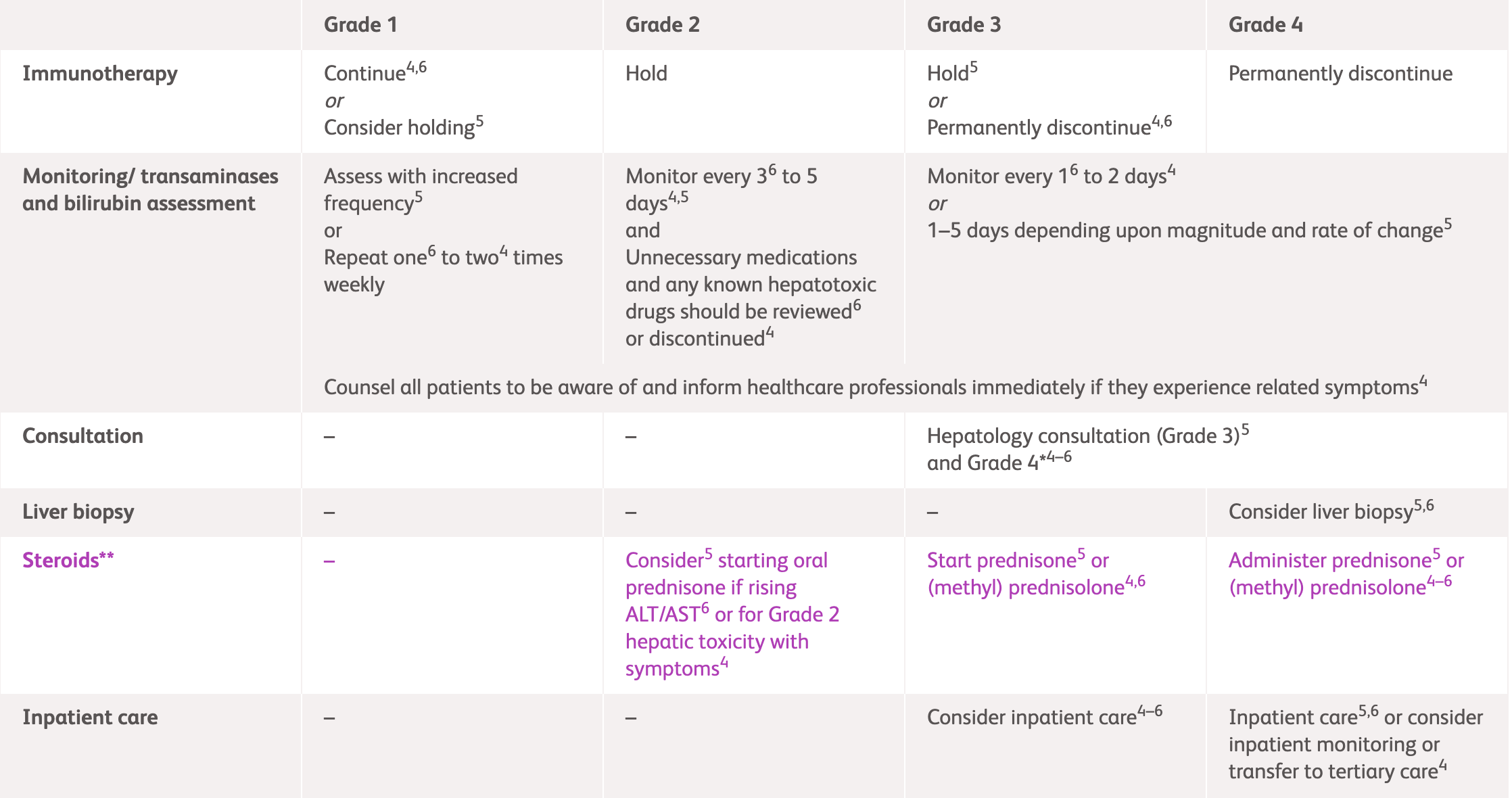
International guideline (NCCN, ESMO and ASCO) recommendations for hepatic irAEs1-3
^For detailed guidelines, please refer to original publication
| NCCN1 | ESMO2 | ASCO3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Consider holding immunotherapy Perform liver tests with increased frequency |
Continue immunotherapy Assess every 1-2 weeks |
Continue immunotherapy Assess 1-2 times weekly |
|
| Grade 2 | Hold immunotherapy Consider corticosteroid use* |
|||
| Assess every 3-5 days Monitor prothrombin time/international normalised ratio periodically |
Assess twice weekly Consider imaging for metastases and/or clots |
Assess every 3 days Consider hepatology consultation |
||
| Grade 3 | Hold immunotherapy | Discontinue immunotherapy | Consider discontinuing if asymptomatic Permanently discontinue if symptomatic |
|
| Perform liver tests every 1-5 days | Assess daily | Assess every 1-2 days | ||
| Corticosteroid use* Consider hepatology consultation; consider liver biopsy1-3 Consider inpatient care1-3, and tertiary care if necessary3 |
||||
| Grade 4 | Discontinue immunotherapy | Discontinue immunotherapy | Consider discontinuing if asymptomatic Permanently discontinue if symptomatic |
|
| Assess 1-3 days | Assess daily | Assess every 1-2 days | ||
| Corticosteroid use* Consider hepatology consultation; consider liver biopsy1-3 Consider inpatient care1-3, and tertiary care if necessary3 |
||||
*Consult steroid usage table below for more information
ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
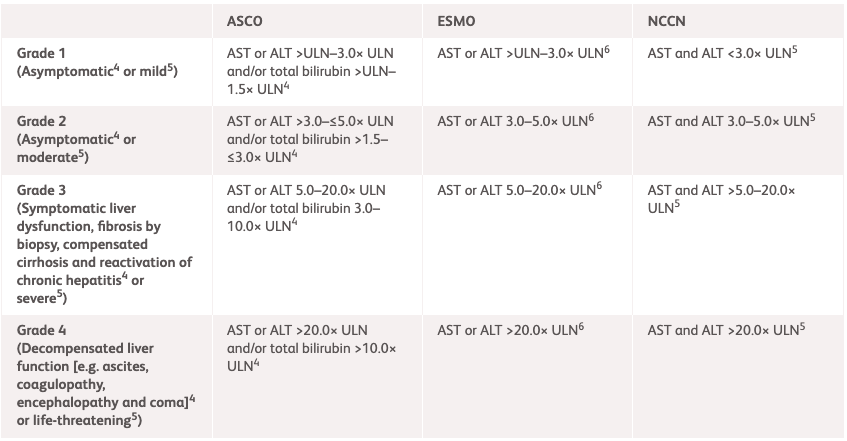
| NCCN1 | ESMO2 | ASCO3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | AST and ALT <3.0× ULN | AST or ALT >ULN-3.0× ULN | AST or ALT >ULN-3.0× ULN and/or total bilirubin >ULN-1.5× ULN |
| Grade 2 | AST and ALT 3.0-5.0× ULN | AST or ALT 3.0-5.0× ULN | AST or ALT >3.0–≤5.0× ULN and/or total bilirubin >1.5–≤3.0× ULN |
| Grade 3 | AST and ALT >5.0–20.0× ULN | AST or ALT 5.0–20.0× ULN | AST or AST or ALT 5.0–20.0× ULN and/or total bilirubin 3.0–10.0× ULN or symptomatic liver dysfunction; fibrosis by biopsy; compensated cirrhosis; and reactivation of chronic hepatitis |
| Grade 4 | AST and ALT >20.0× ULN | AST or ALT >20.0× ULN | AST or AST or ALT >20.0× ULN and/or total bilirubin >10.0× ULN or decompensated liver function (eg, ascites, coagulopathy, encephalopathy, and coma) |
ALT, alanine transaminase; ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; ULN, upper limit of normal.
|
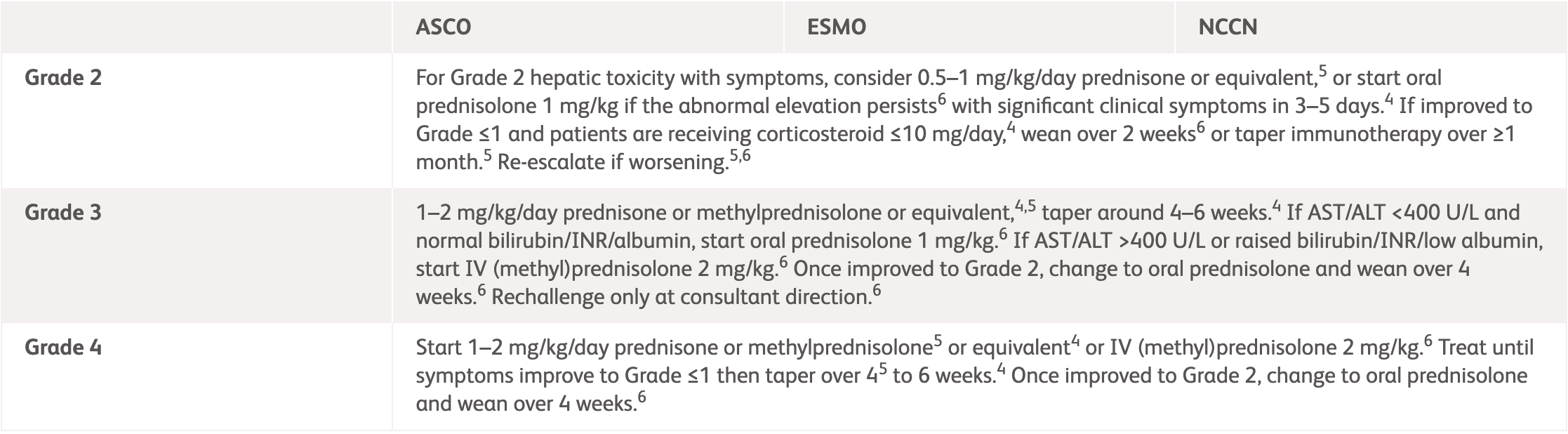
NCCN, ESMO, ASCO1-3 |
|
|---|---|
| Grade 2 | Consider prednisone 0.5–1 mg/kg/day or equivalent.1-3 If improved to Grade ≤1 and patients are receiving corticosteroid, wean over 2-4 weeks.1-3 Re-escalate if worsening.1-3 |
| Grade 3 | 1–2 mg/kg/day prednisone or methylprednisolone or equivalent,1-3 taper around 4-6 weeks.1,3 If AST/ALT <400 U/L and normal bilirubin/INR/albumin, start corticosteroid 1-2 mg/kg.2 If AST/ALT >400 U/L or raised bilirubin/INR/low albumin, start IV (methyl)prednisolone 2 mg/kg.2 Once improved to Grade 2, change to oral prednisolone and wean over 4 weeks.2 Rechallenge only at consultant direction.2 |
| Grade 4 | 1 mg/kg/day prednisone1 or 1–2 mg/kg IV methylprednisolone or equivalents1-3. Treat until symptoms improve then taper over 4-6 weeks.1-3 Once improved to Grade 2, change to oral prednisolone and wean over 4 weeks.2 |
ALT, alanine transaminase; ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; INR, international normalized ratio of prothrombin time; IV, intravenous; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
MMF treatment can be considered in patients who have persistent hepatitis despite high-dose corticosteroids (e.g., 2 mg IV methylprednisolone).1,2 Tocilizumab, tacrolimus, azathioprine, cyclosporine or anti-thymocyte globulin can also be considered.1,2 Infliximab is contraindicated for immune-related hepatitis.1-3
IV, intravenous; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil.
ASCO, American Society of Clinical Oncology; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; irAE, immune-related adverse event; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
References:
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Management of immunotherapy-Related Toxicities. Version 1.2025. Available: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/immunotherapy.pdf. Accessed April 2025.
- Haanen J, et al. Ann Oncol 2022;33:1217–1238. Available at: https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(22)04187-4/fulltext. Accessed March 2025.
- Schneider BJ, et, al. J Clin Oncol 2021;39:4073–4126. Available at: https://ascopubs.org/doi/full/10.1200/JCO.21.01440. Accessed March 2025.
- OPDIVO® (nivolumab) Product Information, BMS Hong Kong.
- YERVOY® (ipilumab) Product Information, BMS Hong Kong.